Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamada, Taichi; Oya, Akihisa*
Keisoku Jido Seigyo Gakkai Rombunshu, 52(12), p.661 - 670, 2016/12
This paper introduces a laser-scanner measurement model using the statistic of laser-scanner data collected in advance for a mobile robot localization. In autonomous navigation, robots usually run based on self position in a map, and laser-scanners are useful sensors for localization. However, in human living environments like urban areas and parks, laser-scanner data is unstable due to moving objects and natural objects, and it is difficult to obtain landmarks like fixed objects. Therefore, our method make a map using statistics of laser-scanner data and calculates the laser-scanner measurement model based on the statistics. Our method is applied to Monte Carlo localization/particlelter. Because the map makes possible to use the frequency and distribution of laser-scanner data for localization, our method allows a robust localization for unstable laser scanner data. In extensive experiments, our method presented an accurate localization and a robot using our method ran stably in actual sidewalks.
Kobayashi, Takuya; Chino, Masamichi; Togawa, Orihiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 43(5), p.569 - 575, 2006/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:24.08(Nuclear Science & Technology)A dissolved radionuclide migration code system that consists of a ocean circulation model, Princeton Ocean Model, and a particle random-walk model, SEA-GEARN, has been developed. The oceanic migration of  Cs discharged from a nuclear submarine in a hypothetical accident at the Tsushima Strait was calculated in the southwestern area of the Japan Sea as a model application. The calculations for instantaneous releases every 10 days were carried out for one year to study the seasonal differences of migration process of the dissolved radionuclides. The migration tendencies of dissolved radionuclides were divided into two patterns. For the releases started from January to September, all of the high concentration areas migrated to the northeast along the coastline of the Main Island of Japan from the release point. As for the releases from October to December, some high concentrations areas migrated to the west from the release point and the concentrations of
Cs discharged from a nuclear submarine in a hypothetical accident at the Tsushima Strait was calculated in the southwestern area of the Japan Sea as a model application. The calculations for instantaneous releases every 10 days were carried out for one year to study the seasonal differences of migration process of the dissolved radionuclides. The migration tendencies of dissolved radionuclides were divided into two patterns. For the releases started from January to September, all of the high concentration areas migrated to the northeast along the coastline of the Main Island of Japan from the release point. As for the releases from October to December, some high concentrations areas migrated to the west from the release point and the concentrations of  Cs along the coastline of the Main Island of Japan were comparatively low.
Cs along the coastline of the Main Island of Japan were comparatively low.
Terada, Hiroaki; Chino, Masamichi
Proceedings of 2nd International Conference on Radioactivity in the Environment, p.15 - 18, 2005/10
The previous version of Worldwide version of System for Prediction of Environmental Emergency Dose Information (WSPEEDI) has been composed of mass-consistent wind field model WSYNOP and particle dispersion model GEARN. Because WSYNOP has no capability to predict meteorological fields, its accuracy and resolution depends on meteorological input data, and it is impossible to treat physical processes realistically. To improve these problems, an atmospheric dynamic model MM5 is introduced and applied to the Chernobyl accident for the verification. Two calculation cases are conducted, CASE-1 a calculation for European region Domain-1, and CASE-2 a domain nesting calculation for Domain-1 and the region around Chernobyl Domain-2. The air concentration and surface deposition of  Cs calculated by CASE-1 agree well with the measurements by statistical analysis and comparison for the horizontal distribution. In the result of CASE-2, the detailed distribution of surface
Cs calculated by CASE-1 agree well with the measurements by statistical analysis and comparison for the horizontal distribution. In the result of CASE-2, the detailed distribution of surface  Cs deposition around Chernobyl which was impossible to calculate in CASE-1 is predicted with high accuracy.
Cs deposition around Chernobyl which was impossible to calculate in CASE-1 is predicted with high accuracy.
Matsumoto, Taro; Naito, Hiroshi*; Tokuda, Shinji; Kishimoto, Yasuaki
Physics of Plasmas, 12(9), p.092505_1 - 092505_7, 2005/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:6.85(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The behavior of the collisionless magnetohydrodynamics modes is investigated by the gyro-kinetic particle simulation in a cylindrical tokamak plasma in the parameter region where the effects of electron inertia and electron parallel compressibility are competitive for magnetic reconnection. Although the linear growth of the 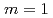 internal kink-tearing mode is dominated by the electron inertia, it is found that the growth rate can be nonlinearly accelerated due to the electron parallel compressibility proportional to the ion sound Larmor radius
internal kink-tearing mode is dominated by the electron inertia, it is found that the growth rate can be nonlinearly accelerated due to the electron parallel compressibility proportional to the ion sound Larmor radius 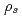 . It is also found that, as decreasing the electron skin depth
. It is also found that, as decreasing the electron skin depth 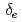 , the maximum growth rate before the internal collapse saturates independently of the microscopic scales such as
, the maximum growth rate before the internal collapse saturates independently of the microscopic scales such as 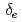 and
and 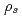 . The acceleration of growth rate is also observed in the nonlinear phase of the
. The acceleration of growth rate is also observed in the nonlinear phase of the 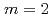 double tearing mode.
double tearing mode.
 Cs deposition due to the Chernobyl nuclear accident
Cs deposition due to the Chernobyl nuclear accidentTerada, Hiroaki; Chino, Masamichi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 42(7), p.651 - 660, 2005/07
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:74.82(Nuclear Science & Technology)The prediction performance of WSPEEDI (Worldwide version of System for Prediction of Environmental Emergency Dose Information), which consists of the atmospheric dynamic model MM5 and the Lagrangian particle dispersion model GEARN-new, is evaluated by measurements of precipitation and surface deposition of  Cs over Europe during the Chernobyl accident. It is concluded that MM5/GEARN-new can predict
Cs over Europe during the Chernobyl accident. It is concluded that MM5/GEARN-new can predict  Cs deposition distribution with good accuracy when accurate precipitation is predicted by using a explicit scheme on cloud microphysics with ice phase processes. High-resolutional calculation is also conducted for the area surrounding Chernobyl by a nesting method. MM5/GEARN-new can predict quite a realistic distribution of
Cs deposition distribution with good accuracy when accurate precipitation is predicted by using a explicit scheme on cloud microphysics with ice phase processes. High-resolutional calculation is also conducted for the area surrounding Chernobyl by a nesting method. MM5/GEARN-new can predict quite a realistic distribution of  Cs deposition around Chernobyl which was not calculated by the previous version.
Cs deposition around Chernobyl which was not calculated by the previous version.
Terada, Hiroaki; Furuno, Akiko; Chino, Masamichi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(5), p.632 - 640, 2004/05
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:79.05(Nuclear Science & Technology)The new version of WSPEEDI (Worldwide version of System for Prediction of Environmental Emergency Dose Information) is developed by introducing the combination of models, the atmospheric dynamic model MM5 and the Lagrangian particle dispersion model GEARN-new to improve the prediction capability. One of the improvements by the new system is that Environmental contaminations in multi domains are predicted simultaneously, and the other is that more precise physical processes are considered by using predicted meteorological conditions with high resolution in time and space. The performance of the system is evaluated for the test calculations of hypothetical nuclear accident in the East Asia region and the Chernobyl accident. The results of test calculation in East Asia seem to be reasonable and the calculated surface air concentrations of  Cs from Chernobyl show good agreement with measurements.
Cs from Chernobyl show good agreement with measurements.
Ueta, Shohei; Sumita, Junya; Emori, Koichi; Takahashi, Masashi*; Sawa, Kazuhiro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 40(9), p.679 - 686, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:64.64(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Sawa, Kazuhiro; Tobita, Tsutomu*
Nuclear Technology, 142(3), p.250 - 259, 2003/06
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:64.64(Nuclear Science & Technology)The maximum burnup of the first-loading fuel of the HTTR is limited to 3.6%FIMA to certify its integrity during the operation. In order to investigate fuel behavior under extended burnup condition, irradiation tests were performed. The thickness of buffer and SiC layers of the irradiated fuel particles were increased to keep their integrity up to over 5%FIMA. The fuel compacts were irradiated in independent capsules at the HFIR of ORNL, and at the JMTR of JAERI, respectively. The comparison of measured and calculated (R/B)s showed that additional failures occurred in both irradiation tests. A pressure vessel failure model analysis showed that no tensile stresses acted on the SiC layers even at the end of irradiation and no pressure vessel failure occurred in the intact particles. The presumed failure mechanisms are additional through-coatings failure of as-fabricated SiC-failed particles or an excessive increase of internal pressure by the accelerated irradiation. The further study is needed to clarify the failure mechanism.
Takizuka, Tomonori; Hosokawa, Masanari*; Shimizu, Katsuhiro
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 313-316(1-3), p.1331 - 1334, 2003/03
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:68.99(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In course of tokamak fusion research, particle and heat control is one of the most crucial issues. Helium ash exhaust and impurity retention in the divertor region owe to the plasma flow towards divertor plate. The localization of heat load on the plate depends on the flow pattern. Accordingly, particle and heat control can be achieved by the proper control of the flow in SOL and divertor plasmas. In this paper, the flow control is studied with two-dimensional particle simulations by PARASOL (PARticle Advanced simulation for SOL and divertor plasmas) code. Magnetic field configuration with separatrix like a tokamak divertor configuration is given. Hot particle source is put in the core plasma. Recycling cold particle source is located near the divertor plate. Particle source of gas puff in the SOL plasma is given for the flow control. Divertor biasing is available by changing the electrostatic potential on the plates. Effects of gas puff and biasing on the flow are studied. Controllability is evaluated from simulation results.
Kobayashi, Takuya; Nagai, Haruyasu; Chino, Masamichi; Togawa, Orihiko
Proceedings of International Symposium on Radioecology and Environmental Dosimetry, p.500 - 504, 2003/00
The possibility of radionuclide release to the environment is on the increase due to a growth of nuclear facilities in Asia, military problems, nuclear terrorism, etc. The released radionuclides circulate among the atmospheric, oceanic and terrestrial environment, influencing human and natural environment through complex processes. In order to reduce the damage from these pollutants, it is necessary to estimate their migration behavior in detail. A software system SPEEDI-MP (SPEEDI Multi-model Package) is under development to resolve such environmental problems by simulating the 'inclusive and successive' behavior of pollutants in the atmospheric, oceanic and terrestrial environment. As code verification, the system has been applied to a hypothetical accident of a nuclear submarine if it sinks in an offshore region around Japan. The predicted results are examined, and the applicability and validity of the system are discussed.
Terada, Hiroaki; Furuno, Akiko; Chino, Masamichi
Proceedings from the International Conference on Radioactivity in the Environment (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2002/09
The present study aims to expanding the capability of WSPEEDI, so that it can be applied to atmospheric releases of radionuclides in the world for terrorist attack as well as nuclear accident. A terrorist attack would be possible in any time, any place and any scale. Altough WSPEEDI has already had a function to acquire global meteorological forecasts to generate a geographical map at arbitrary region in the world, it had no capability for simultaneous multi-scale predictions. Thus, the combination of models, non-hydrostatic meteorological model MM5 and atmospheric dispersion model GEARN, is introduced to WSPEEDI. MM5 can forecast local and regional meteorological condition simultaneously by domain nesting calculations. By the input of meteorological condition generated by MM5, GEARN can forecast multi-scale environmental contaminations considering detailed boundary layer and precipitation processes. Using this improved WSPEEDI, we made test calculations assuming a nuclear accident or terrorist attack in Asia.
Kobayashi, Takuya; Lee, S.; Chino, Masamichi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 39(2), p.171 - 179, 2002/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:23.39(Nuclear Science & Technology)A three-dimensional model system was developed to predict oceanic dispersions of radionuclides released into the eastern area of Shimokita Peninsula. This system is a combination of the Princeton Ocean Model (POM) for predicting ocean currents and a particle random walk model for oceanic dispersion of radionuclides. The model was verified by using measured currents, temperature and salinity at the coastal area of Shimokita, Aomori-ken, Japan, where a nuclear fuel reprocessing plant is under construction. The results obtained from simulations area as follows; (1) Wind and the Tsugaru Warm Current entering into the objective region through the Tsugaru Strait significantly affect the structure of current over the region. (2) POM can represent seasonal variations of the Tsugaru Warm Current well with hypothetical oceanographic data. The calculation succeeded to reproduce the coastal mode from winter to spring and the gyre mode from summer to autumn.
Sawa, Kazuhiro; Ueta, Shohei; Sumita, Junya; Verfondern, K.*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 38(6), p.411 - 419, 2001/06
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:74.75(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Martin, D. G.*; Sawa, Kazuhiro; Ueta, Shohei; Sumita, Junya
JAERI-Research 2001-033, 19 Pages, 2001/05
no abstracts in English
Sawa, Kazuhiro; Yoshimuta, Shigeharu*; Tobita, Tsutomu*;
JAERI-Research 97-036, 23 Pages, 1997/05
no abstracts in English
Sawa, Kazuhiro; Minato, Kazuo; Tobita, Tsutomu*; Fukuda, Kosaku
Nuclear Technology, 118(2), p.123 - 131, 1997/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:14.47(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Sawa, Kazuhiro; Minato, Kazuo; Fukuda, Kosaku
JAERI-Research 96-063, 34 Pages, 1996/11
no abstracts in English
Sawa, Kazuhiro; Shiozawa, Shusaku; Minato, Kazuo; Fukuda, Kosaku
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 33(9), p.712 - 720, 1996/09
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:86.64(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Murata, Isao; Mori, Takamasa; Nakakawa, Masayuki
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 123, p.96 - 109, 1996/00
Times Cited Count:38 Percentile:92.97(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 F+
F+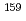 Tb reaction
Tb reactionIkezoe, Hiroshi; Nagame, Yuichiro; *; Sugiyama, Yasuharu; Tomita, Yoshiaki; Ideno, K.; Hamada, S.; ; Iwamoto, Akira; *
Physical Review C, 49(2), p.968 - 976, 1994/02
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:79.67(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English